When you think of the greatest minds in history, Albert Einstein undoubtedly comes to mind. His name has become synonymous with genius, and his contributions to science have left an indelible mark on the world. Born in 1879 in Ulm, Germany, Einstein’s journey from a curious child to a revolutionary physicist is a testament to the power of imagination and intellect.
His work not only transformed our understanding of the universe but also reshaped the very fabric of scientific inquiry. As you delve into the intricacies of his theories and their implications, you will discover how Einstein’s legacy continues to influence various fields, from physics to philosophy. Einstein’s life was characterized by a relentless pursuit of knowledge and a profound curiosity about the nature of reality.
His theories have not only advanced scientific thought but have also inspired generations of thinkers, scientists, and dreamers. As you explore the various dimensions of Einstein’s legacy, you will come to appreciate how his work transcends time and continues to resonate in contemporary discussions about science and its role in society.
Key Takeaways
- Einstein’s theory of relativity revolutionized our understanding of space, time, and gravity, and continues to shape modern physics.
- The equation E=mc^2, derived from Einstein’s theory of relativity, has had a profound impact on the fields of nuclear physics and energy production.
- Einstein’s work on quantum mechanics laid the foundation for the quantum revolution, challenging traditional views of determinism and causality.
- Einstein’s influence on modern cosmology is evident in his contributions to the study of the expanding universe and the concept of dark matter.
- Einstein’s involvement in the development of the atomic bomb raised ethical and philosophical questions about the responsibility of scientists in the pursuit of knowledge.
Einstein’s Theory of Relativity
At the heart of Einstein’s contributions lies his Theory of Relativity, which fundamentally altered our understanding of space, time, and gravity. You may be familiar with the two main components of this theory: Special Relativity and General Relativity. Special Relativity, introduced in 1905, revolutionized the way we perceive time and space by asserting that the laws of physics are the same for all observers, regardless of their relative motion.
This radical idea led to the conclusion that time is not an absolute entity but rather a dimension that can be affected by speed. As you ponder this concept, consider how it challenges your everyday experiences and perceptions. General Relativity, published in 1915, took these ideas further by describing gravity not as a force but as a curvature of spacetime caused by mass.
This groundbreaking perspective reshaped our understanding of celestial mechanics and provided a framework for understanding phenomena such as black holes and gravitational waves. As you reflect on these concepts, you may find yourself marveling at how Einstein’s insights have paved the way for modern astrophysics and cosmology. The implications of his theories extend far beyond theoretical physics; they have practical applications in technologies such as GPS systems, which rely on adjustments for relativistic effects.
The Impact of E=mc^2
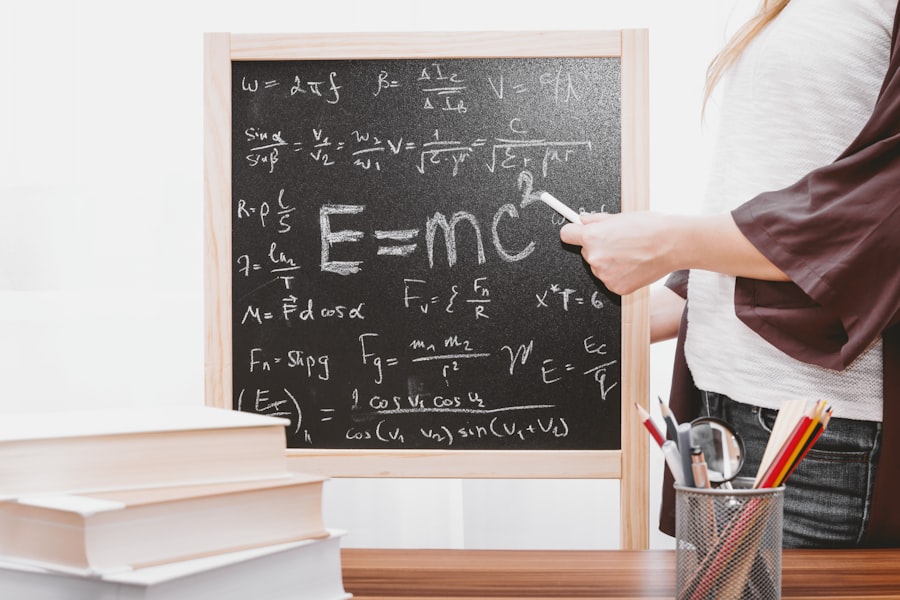
One of the most famous equations in history, E=mc^2, encapsulates the essence of Einstein’s revolutionary ideas about energy and mass. This equation expresses the equivalence between mass (m) and energy (E), with “c” representing the speed of light in a vacuum. As you contemplate this equation, consider its profound implications: it suggests that a small amount of mass can be converted into a tremendous amount of energy.
This realization not only transformed theoretical physics but also had far-reaching consequences for technology and society. The impact of E=mc^2 extends into various domains, including nuclear energy and weaponry. The equation laid the groundwork for understanding nuclear fission and fusion processes, which are at the heart of both nuclear power generation and atomic bombs.
As you explore these developments, you may grapple with the ethical implications of harnessing such powerful energy sources. The duality of E=mc^2—its potential for both creation and destruction—serves as a reminder of the responsibility that comes with scientific discovery.
The Quantum Revolution
| Metrics | Data |
|---|---|
| Number of Quantum Computers | 100+ |
| Quantum Volume | Over 100 |
| Investment in Quantum Technologies | Billions of dollars |
| Number of Quantum Algorithms | Dozens |
| Quantum Computing Market Size | Projected to reach 65 billion by 2030 |
While Einstein is often celebrated for his contributions to relativity, his relationship with quantum mechanics is equally fascinating. You might find it intriguing that despite being one of the pioneers in this field, Einstein had reservations about some of its interpretations.
This tension between determinism and probability is a central theme in your exploration of modern physics. The quantum revolution fundamentally changed how scientists understand the behavior of particles at the atomic and subatomic levels. Concepts such as wave-particle duality and quantum entanglement challenge traditional notions of causality and locality.
As you delve deeper into these ideas, you may appreciate how they have led to technological advancements like semiconductors and quantum computing. Despite his skepticism, Einstein’s work laid essential groundwork for future developments in quantum theory, demonstrating that even great minds can grapple with complex ideas that challenge their beliefs.
Einstein’s Influence on Modern Cosmology
Einstein’s contributions extend far beyond theoretical physics; they have profoundly influenced modern cosmology as well. His General Theory of Relativity provided the framework for understanding the large-scale structure of the universe. You may find it fascinating that Einstein initially resisted the idea of an expanding universe, introducing a cosmological constant to maintain a static model.
However, subsequent observations by astronomers like Edwin Hubble revealed that the universe is indeed expanding, leading Einstein to famously refer to his cosmological constant as his “greatest blunder.” As you explore modern cosmology, consider how Einstein’s theories have shaped our understanding of phenomena such as dark matter and dark energy. These concepts are crucial for explaining the universe’s accelerated expansion and its overall structure. The interplay between Einstein’s work and contemporary cosmological research highlights how scientific inquiry is an evolving process, where new discoveries build upon foundational theories.
Your appreciation for this dynamic nature of science will deepen as you recognize how Einstein’s legacy continues to inform our quest to understand the cosmos.
Einstein’s Contributions to the Development of the Atomic Bomb

One cannot discuss Einstein’s legacy without acknowledging his indirect role in the development of the atomic bomb during World War
While he did not work directly on the Manhattan Project, his letter to President Franklin D. Roosevelt in 1939 warned about the potential for Nazi Germany to develop nuclear weapons. This letter played a pivotal role in initiating U.S.
government interest in atomic research. As you reflect on this historical context, consider the moral complexities surrounding scientific discovery and its applications.
The atomic bomb represents a dual-edged sword: it was a technological marvel that ended World War II but also ushered in an era marked by nuclear proliferation and existential threats. You may find it compelling to explore how Einstein later expressed regret over his involvement in promoting nuclear weapons development. His advocacy for peace and disarmament highlights the ethical responsibilities that accompany scientific advancements.
As you contemplate these issues, you will gain insight into the broader implications of scientific progress on society.
Einstein’s Influence on the Philosophy of Science
Einstein’s work has not only shaped scientific thought but has also significantly influenced the philosophy of science. His ideas challenge traditional notions about observation, reality, and the nature of scientific theories. You might find it intriguing that Einstein believed that scientific theories should be grounded in empirical observations while also possessing an underlying simplicity and elegance.
This perspective invites you to consider how scientific inquiry balances creativity with rigorous experimentation. Moreover, Einstein’s emphasis on theoretical frameworks has sparked discussions about realism versus instrumentalism in science. As you engage with these philosophical debates, you may appreciate how Einstein’s legacy encourages critical thinking about the nature of knowledge itself.
His insistence on questioning established norms serves as a reminder that scientific progress often arises from challenging prevailing assumptions.
Einstein’s Legacy in the Field of Astrophysics
In addition to his contributions to theoretical physics and cosmology, Einstein’s work has had a lasting impact on astrophysics as well. His theories have provided essential tools for understanding celestial phenomena such as black holes, neutron stars, and gravitational waves. You may find it fascinating that recent discoveries in astrophysics—such as the detection of gravitational waves by LIGO—are direct confirmations of predictions made by Einstein over a century ago.
As you explore these advancements, consider how they have expanded our understanding of the universe’s fundamental workings. The interplay between theory and observation in astrophysics exemplifies how Einstein’s legacy continues to inspire new generations of scientists seeking answers to profound questions about existence and our place in the cosmos.
The Continuing Relevance of Einstein’s Work in Physics
Even more than a century after his most significant contributions, Einstein’s work remains relevant in contemporary physics research. The principles he established continue to guide investigations into fundamental questions about matter, energy, space, and time. You may find it remarkable that ongoing research into areas like quantum gravity seeks to reconcile general relativity with quantum mechanics—an endeavor that reflects Einstein’s enduring influence on modern scientific inquiry.
As you engage with current developments in physics, consider how scientists are still grappling with challenges posed by Einstein’s theories. The quest for a unified theory that encompasses both relativity and quantum mechanics remains one of the most significant pursuits in contemporary physics. Your exploration of these topics will reveal how Einstein’s legacy serves as both a foundation for current research and a source of inspiration for future breakthroughs.
Einstein’s Influence on the Public Understanding of Science
Einstein’s impact extends beyond academia; he has played a crucial role in shaping public perceptions of science as well. His iconic image—a wild-haired genius—has become emblematic of intellectual curiosity and creativity. You might find it interesting how his ability to communicate complex ideas in accessible terms has made science more relatable to the general public.
Through lectures, writings, and public appearances, Einstein fostered a sense of wonder about scientific exploration. Moreover, his advocacy for social issues—such as pacifism, civil rights, and education—has further solidified his status as a public intellectual who transcended disciplinary boundaries. As you reflect on these aspects of his legacy, consider how Einstein’s life story encourages individuals from all walks of life to engage with science critically and thoughtfully.
Einstein’s Enduring Impact on Scientific Thought
In conclusion, Albert Einstein’s legacy is multifaceted and enduring, influencing not only physics but also philosophy, ethics, and public understanding of science. His revolutionary theories have reshaped our comprehension of reality while inspiring generations to think critically about complex issues facing humanity today. As you contemplate his contributions—from relativity to quantum mechanics—you will recognize that Einstein’s work transcends time; it continues to challenge our perceptions and inspire curiosity about the universe.
As you navigate through your own journey in science or any field that piques your interest, let Einstein’s example serve as a guiding light—a reminder that questioning established norms can lead to profound discoveries that shape our understanding of existence itself. His legacy is not merely confined to textbooks; it lives on in every inquiry that seeks to unravel the mysteries of our world.
Albert Einstein’s legacy continues to influence the world of physics and beyond, inspiring countless researchers and enthusiasts to explore the mysteries of the universe. His groundbreaking theories, particularly the theory of relativity, have paved the way for numerous scientific advancements. For those interested in delving deeper into the impact of Einstein’s work, a related article can be found on My Cosmic Ventures. This article explores how Einstein’s theories have shaped modern scientific thought and continue to inspire new generations of scientists. To read more about this fascinating topic, visit the article on My Cosmic Ventures.
FAQs
What is Einstein’s legacy?
Einstein’s legacy refers to the impact and influence of the work and theories of physicist Albert Einstein on the field of physics and the broader scientific community.
What are some of Einstein’s most famous contributions?
Some of Einstein’s most famous contributions include the theory of relativity, the equation E=mc^2, and his work on the photoelectric effect, which helped to establish the field of quantum mechanics.
How did Einstein’s work on the theory of relativity change our understanding of the universe?
Einstein’s theory of relativity fundamentally changed our understanding of space, time, and gravity. It provided a new framework for understanding the behavior of objects in the universe, particularly at high speeds or in strong gravitational fields.
What impact did Einstein’s work have on the development of modern technology?
Einstein’s work on the theory of relativity and his contributions to quantum mechanics have had a profound impact on the development of modern technology, particularly in the fields of nuclear energy, GPS systems, and the development of new materials.
How has Einstein’s legacy influenced the field of physics and scientific research?
Einstein’s legacy has had a lasting influence on the field of physics and scientific research, inspiring new generations of scientists and leading to further advancements in our understanding of the universe. His work continues to be a source of inspiration and exploration for physicists and researchers around the world.
