Black holes are among the most enigmatic and fascinating phenomena in the universe. They are regions in space where the gravitational pull is so intense that nothing, not even light, can escape from them. This characteristic makes black holes invisible to traditional observational methods, leading to their classification as “black.” The formation of black holes typically occurs when massive stars exhaust their nuclear fuel and undergo gravitational collapse, resulting in a singularity—a point of infinite density—surrounded by an event horizon, which marks the boundary beyond which nothing can return.
The study of black holes has evolved significantly since their theoretical inception in the early 20th century. Albert Einstein’s general theory of relativity laid the groundwork for understanding how mass and energy warp spacetime, leading to the prediction of these cosmic giants. Over the decades, astronomers have identified various types of black holes, including stellar black holes, which form from collapsing stars, and supermassive black holes, which reside at the centers of galaxies and can contain millions to billions of solar masses.
Key Takeaways
- Black holes are regions in space where the gravitational pull is so strong that nothing, not even light, can escape.
- Predicting black hole trajectory is important for understanding their behavior and potential impact on surrounding objects.
- Observing black holes requires advanced tools such as telescopes, X-ray detectors, and radio telescopes.
- Factors affecting black hole trajectory include mass, spin, and the presence of nearby objects.
- Gravitational waves play a crucial role in predicting black hole trajectory and understanding their behavior in space.
The Importance of Predicting Black Hole Trajectory
Predicting the trajectory of black holes is crucial for several reasons, particularly in understanding their interactions with surrounding celestial bodies and their influence on galactic dynamics. As black holes move through space, they can affect the orbits of nearby stars and gas clouds, leading to significant changes in the structure and behavior of galaxies. By accurately predicting these trajectories, astronomers can gain insights into the evolution of galaxies and the role that black holes play in shaping cosmic structures.
Moreover, understanding black hole trajectories is essential for anticipating potential gravitational wave events. When two black holes collide or merge, they emit ripples in spacetime known as gravitational waves. These waves carry information about the properties of the black holes involved and their dynamics.
By predicting when and where these events might occur, scientists can prepare for observations with gravitational wave detectors like LIGO and Virgo, enhancing our understanding of fundamental physics and the universe’s history.
Tools and Techniques for Observing Black Holes
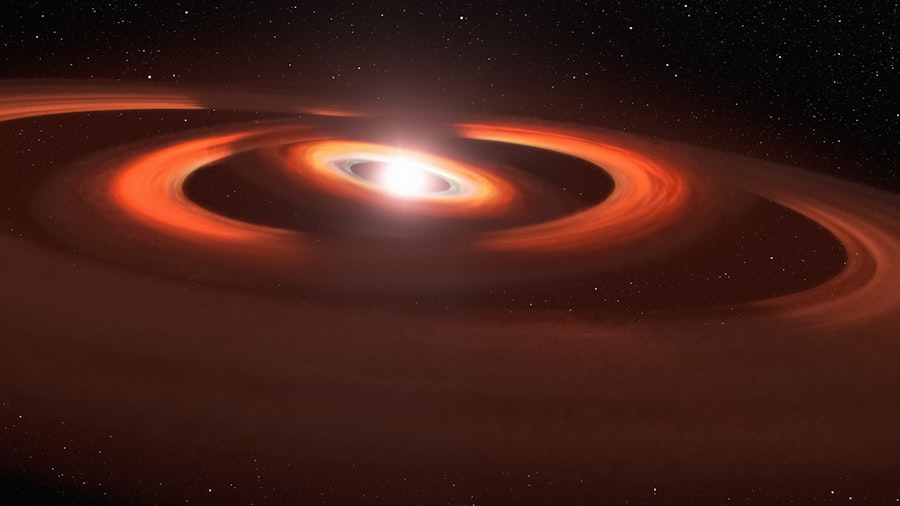

The observation of black holes presents unique challenges due to their inherent invisibility. However, astronomers have developed a range of tools and techniques to study these elusive objects indirectly. One of the primary methods involves observing the effects of a black hole’s gravity on nearby stars and gas.
By tracking the motion of these objects, scientists can infer the presence of a black hole and estimate its mass. This technique has been instrumental in identifying supermassive black holes at the centers of galaxies. In addition to traditional optical telescopes, astronomers utilize radio telescopes and X-ray observatories to gather data on black holes.
For instance, X-ray emissions from accretion disks—hot gas spiraling into a black hole—can provide valuable information about its properties. The Event Horizon Telescope (EHT) represents a groundbreaking advancement in this field, as it combines data from multiple radio telescopes around the world to create high-resolution images of black holes’ event horizons. This innovative approach has allowed scientists to capture the first-ever image of a black hole in 2019, marking a significant milestone in astrophysics.
Factors Affecting Black Hole Trajectory
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Mass of the Black Hole | The larger the mass, the stronger the gravitational pull affecting the trajectory. |
| Speed of the Black Hole | The velocity of the black hole can affect the trajectory of objects around it. |
| Proximity to Other Massive Objects | Other nearby massive objects can influence the trajectory of a black hole. |
| Angular Momentum | The rotation of the black hole can affect the trajectory of objects near it. |
Several factors influence the trajectory of black holes as they traverse space. One primary factor is gravitational interactions with other celestial bodies. When a black hole passes near another star or a cluster of stars, its gravitational pull can alter their orbits and lead to complex dynamical interactions.
These encounters can result in phenomena such as star ejections or even the capture of stars by the black hole’s gravity. Another critical factor is the environment surrounding a black hole. In dense regions like star clusters or galactic centers, interactions with other massive objects can significantly affect a black hole’s trajectory.
Additionally, the presence of dark matter—an invisible substance that makes up a significant portion of the universe’s mass—can also influence how black holes move through space. Understanding these factors is essential for accurately predicting their paths and comprehending their role in cosmic evolution.
The Role of Gravitational Waves in Predicting Black Hole Trajectory
Gravitational waves have revolutionized our understanding of black holes and their dynamics. These ripples in spacetime are produced by accelerating masses, such as merging black holes or neutron stars. When two black holes spiral toward each other and eventually collide, they emit gravitational waves that carry information about their masses, spins, and trajectories.
By analyzing these waves, scientists can reconstruct the events leading up to a merger and gain insights into the properties of the involved black holes. The detection of gravitational waves has opened new avenues for predicting black hole trajectories. Advanced detectors like LIGO and Virgo have enabled astronomers to observe these cosmic events in real-time, allowing for immediate follow-up observations across various wavelengths.
This multi-messenger approach enhances our understanding of black hole mergers and provides valuable data for refining models that predict their trajectories in different environments.
Using Mathematical Models to Predict Black Hole Trajectory
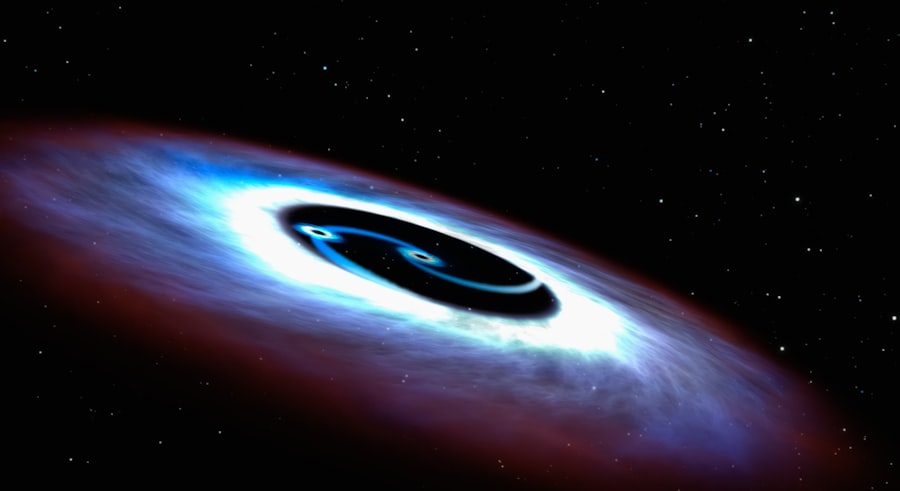

Mathematical models play a pivotal role in predicting black hole trajectories by providing a framework for understanding their motion within the context of general relativity. These models incorporate various parameters such as mass, spin, and surrounding gravitational influences to simulate how a black hole would behave over time. Numerical simulations are particularly valuable in this regard, as they allow scientists to explore complex scenarios that may not be easily solvable analytically.
One common approach involves using N-body simulations to model systems containing multiple black holes or other massive objects. These simulations can reveal how gravitational interactions shape the trajectories of individual black holes over extended periods. By comparing simulation results with observational data, researchers can refine their models and improve predictions regarding future movements and interactions.
Challenges and Limitations in Predicting Black Hole Trajectory
Despite advancements in technology and theoretical understanding, predicting black hole trajectories remains fraught with challenges and limitations. One significant hurdle is the inherent complexity of gravitational interactions in multi-body systems. As more massive objects are introduced into a simulation, the calculations become increasingly intricate, making it difficult to achieve accurate predictions over long timescales.
Additionally, uncertainties in measuring key parameters such as mass and spin introduce further complications. Variations in these parameters can lead to divergent outcomes in trajectory predictions. Moreover, the chaotic nature of gravitational interactions means that small changes in initial conditions can result in vastly different trajectories over time.
This sensitivity poses a challenge for long-term predictions and necessitates ongoing refinement of models based on new observational data.
Collaborative Efforts in Black Hole Trajectory Prediction
The study of black hole trajectories is inherently interdisciplinary, requiring collaboration among astrophysicists, mathematicians, computer scientists, and engineers. Collaborative efforts have become increasingly important as researchers seek to combine expertise from various fields to tackle complex problems associated with black hole dynamics. International collaborations like the LIGO Scientific Collaboration exemplify this trend by bringing together scientists from around the world to share data, resources, and insights.
Furthermore, advancements in computational power have facilitated large-scale simulations that require significant resources and expertise. By pooling knowledge and technology across institutions, researchers can enhance their ability to model intricate systems involving multiple black holes or other massive objects. This collaborative approach not only accelerates progress but also fosters innovation by encouraging diverse perspectives on challenging questions related to black hole trajectories.
The Impact of Predicting Black Hole Trajectory on Astrophysics
The ability to predict black hole trajectories has far-reaching implications for astrophysics as a whole. Understanding how black holes interact with their environments contributes to broader theories about galaxy formation and evolution. For instance, insights gained from trajectory predictions can inform models that explain how supermassive black holes influence star formation rates within galaxies or how they regulate galactic dynamics.
Moreover, accurate predictions enhance our understanding of fundamental physics principles such as gravity and spacetime curvature. By studying how black holes behave under various conditions, researchers can test existing theories and potentially uncover new physics beyond current models. This interplay between observation and theory drives progress in astrophysics and deepens humanity’s understanding of the universe’s fundamental workings.
Future Directions in Black Hole Trajectory Prediction
As technology continues to advance, future directions in predicting black hole trajectories are likely to be shaped by improvements in observational capabilities and computational methods. The next generation of gravitational wave detectors promises to enhance sensitivity and broaden detection ranges, allowing for more frequent observations of merging black holes. This influx of data will provide invaluable opportunities for refining trajectory predictions and testing theoretical models against real-world events.
Additionally, developments in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning hold great potential for revolutionizing trajectory prediction efforts. These technologies can analyze vast datasets more efficiently than traditional methods, identifying patterns that may not be immediately apparent to human researchers. By integrating AI into trajectory prediction workflows, scientists may uncover new insights into black hole dynamics that were previously inaccessible.
Ethical Considerations in Black Hole Trajectory Prediction
As with any scientific endeavor, ethical considerations play a crucial role in predicting black hole trajectories. One primary concern revolves around the potential implications of this research on our understanding of cosmic phenomena and humanity’s place within the universe. As scientists uncover more about black holes and their behaviors, questions arise regarding how this knowledge might influence philosophical perspectives on existence and reality.
Moreover, there are ethical considerations related to resource allocation within scientific research. As funding for astrophysics projects often competes with pressing societal needs such as healthcare or education, researchers must navigate these complexities while advocating for continued investment in fundamental science. Balancing curiosity-driven research with societal responsibilities remains an ongoing challenge for the scientific community as it seeks to advance knowledge while addressing broader ethical concerns.
In conclusion, predicting black hole trajectories is a multifaceted endeavor that encompasses theoretical modeling, observational techniques, collaborative efforts, and ethical considerations. As researchers continue to unravel the mysteries surrounding these cosmic giants, they contribute not only to our understanding of astrophysics but also to humanity’s broader quest for knowledge about the universe we inhabit.
To gain a deeper understanding of how to predict black hole trajectories, you may find it helpful to read the related article on cosmic phenomena. This article provides insights into the methods used by astronomers to track the movement of these enigmatic objects in space. For more information, visit the article here.
WATCH THIS! The Invisible Threat: A Rogue Black Hole Headed for Our Solar System?
FAQs
What is a black hole trajectory?
A black hole trajectory refers to the path or course that a black hole follows through space as it moves and interacts with other celestial bodies.
Why is predicting a black hole trajectory important?
Predicting a black hole’s trajectory is important for understanding its behavior and potential impact on surrounding objects, such as stars and planets. It also helps in studying the dynamics of the universe and the evolution of galaxies.
What factors influence the trajectory of a black hole?
The trajectory of a black hole is influenced by factors such as its mass, the gravitational forces acting upon it, and the presence of other massive objects in its vicinity.
How do scientists predict the trajectory of a black hole?
Scientists use mathematical models and computer simulations to predict the trajectory of a black hole. These models take into account the gravitational forces and interactions with other celestial bodies to forecast the path of the black hole.
What are the challenges in predicting a black hole’s trajectory?
One of the main challenges in predicting a black hole’s trajectory is the complex nature of gravitational interactions in space. Additionally, the presence of other massive objects can also influence the path of a black hole, making accurate predictions more difficult.