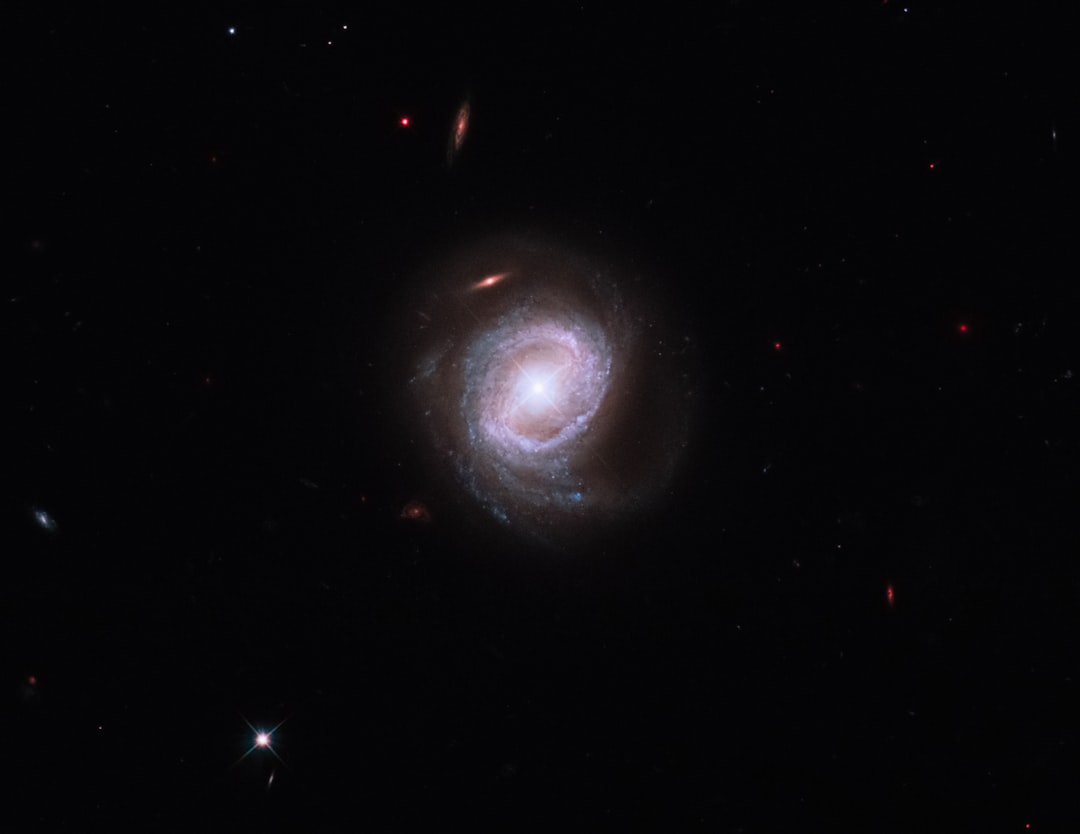
Galaxy alignment filaments represent a fascinating aspect of cosmic structure, revealing the intricate web of the universe. These elongated structures, composed of galaxies and dark matter, are thought to be the result of gravitational interactions and the expansion of the universe. As researchers delve deeper into the cosmos, they uncover the significance of these filaments in understanding the formation and evolution of galaxies.
The alignment of galaxies within these filaments is not merely a random occurrence; it reflects the underlying physics governing cosmic evolution. The study of galaxy alignment filaments has gained momentum in recent years, driven by advancements in observational technology and theoretical modeling. As astronomers map the large-scale structure of the universe, they have begun to recognize patterns that suggest a coherent organization of galaxies along these filaments.
This realization has profound implications for cosmology, as it challenges existing paradigms and invites new questions about the nature of dark matter, galaxy formation, and the overall dynamics of the universe.
Key Takeaways
- Galaxy alignment filaments are large-scale structures influencing the orientation and distribution of galaxies in the universe.
- Dark matter plays a crucial role in shaping and maintaining the structure of galaxy alignment filaments.
- Observational data supports the existence of these filaments and their connection to the cosmic web and large-scale structure.
- Galaxy alignment filaments impact galaxy evolution by affecting galaxy formation, spin, and interaction patterns.
- Studying these filaments offers important insights for cosmology and astrophysics, despite challenges in observation and modeling.
Theoretical Framework for Understanding Galaxy Alignment Filaments
To comprehend galaxy alignment filaments, one must first grasp the theoretical framework that underpins their existence. The Lambda Cold Dark Matter (ΛCDM) model serves as the cornerstone of modern cosmology, positing that dark matter plays a crucial role in shaping the universe’s structure. According to this model, galaxies form and evolve within a cosmic web of dark matter, which acts as a scaffold for visible matter.
This framework suggests that galaxies are not isolated entities but rather part of a larger interconnected system. The gravitational forces exerted by dark matter halos influence the motion and distribution of galaxies, leading to their alignment along filaments. These filaments are thought to arise from the merging and accretion processes that occur in the early universe.
As matter clumps together under gravity, it forms dense regions that eventually evolve into galaxies. The alignment observed in these structures can be attributed to the anisotropic distribution of dark matter, which guides the formation and orientation of galaxies along preferred directions.
Observational Evidence of Galaxy Alignment Filaments
Observational evidence supporting the existence of galaxy alignment filaments has been accumulating through various astronomical surveys. Large-scale surveys such as the Sloan Digital Sky Survey (SDSS) have provided extensive data on galaxy positions and orientations, revealing striking patterns consistent with filamentary structures. Researchers have noted that galaxies tend to align with their neighbors along these filaments, suggesting a coherent organization rather than random distribution.
Moreover, studies utilizing advanced imaging techniques have allowed astronomers to visualize these filaments more clearly. By analyzing galaxy redshift data, scientists can trace the three-dimensional distribution of galaxies and identify filamentary structures in the cosmic web. These observations have confirmed that galaxies are not merely scattered throughout space but are instead organized into vast networks that extend across billions of light-years.
Such findings underscore the importance of galaxy alignment filaments in understanding the large-scale structure of the universe.
The Role of Dark Matter in Galaxy Alignment Filaments
Dark matter plays a pivotal role in shaping galaxy alignment filaments, acting as both a gravitational anchor and a facilitator for galaxy formation. The presence of dark matter halos around galaxies influences their motion and orientation, leading to the observed alignments along filaments. These halos are thought to be composed of non-baryonic matter that interacts primarily through gravity, making them invisible to traditional observational techniques.
The interaction between dark matter and baryonic matter is crucial for understanding how galaxies evolve within filaments. As gas and dust fall into dark matter halos, they cool and condense to form stars, leading to the birth of new galaxies. The gravitational pull from dark matter not only dictates where these galaxies form but also influences their subsequent interactions with neighboring galaxies.
This dynamic interplay between dark and baryonic matter is essential for comprehending the alignment patterns observed in galaxy filaments.
Connection between Galaxy Alignment Filaments and Large Scale Structure of the Universe
| Metric | Description | Typical Value / Range | Unit | Source / Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Galaxy Spin Alignment Angle | Angle between galaxy spin axis and filament direction | 0° to 90° (mean alignment ~30°) | Degrees | Observational studies (e.g., Tempel et al. 2013) |
| Filament Torque Magnitude | Torque exerted by cosmic filaments on galaxy halos | 10^42 to 10^44 | Newton meter (N·m) | Simulation data (e.g., Codis et al. 2015) |
| Galaxy Angular Momentum | Intrinsic angular momentum of galaxies influenced by filaments | 10^67 to 10^69 | kg·m²/s | Theoretical models and simulations |
| Filament Length | Typical length scale of cosmic filaments affecting galaxies | 10 to 100 | Megaparsecs (Mpc) | Large scale structure surveys |
| Galaxy Mass | Mass of galaxies within filaments experiencing torque | 10^10 to 10^12 | Solar masses (M☉) | Galaxy surveys and simulations |
| Alignment Correlation Coefficient | Statistical measure of spin-filament alignment strength | 0.2 to 0.5 | Dimensionless | Statistical analyses (e.g., Libeskind et al. 2013) |
Galaxy alignment filaments are integral to understanding the large-scale structure of the universe. They serve as conduits for matter flow, connecting clusters and superclusters while delineating vast voids between them. This cosmic web structure is a manifestation of gravitational forces at play on a grand scale, where filaments act as highways for galaxy migration and interaction.
The connection between galaxy alignment filaments and large-scale structure is further emphasized by simulations that model cosmic evolution. These simulations reveal how initial density fluctuations in the early universe led to the formation of filaments, clusters, and voids over billions of years. By studying these simulations alongside observational data, researchers can gain insights into how galaxies evolve within this intricate framework, shedding light on their formation history and future trajectories.
Impact of Galaxy Alignment Filaments on Galaxy Evolution

The presence of galaxy alignment filaments significantly impacts galaxy evolution by influencing star formation rates, morphological characteristics, and interactions among galaxies. Galaxies situated within filaments often experience enhanced star formation due to increased gas density and gravitational interactions with neighboring galaxies. This environment fosters conditions conducive to rapid stellar growth, leading to diverse galactic morphologies.
These processes can result in changes to a galaxy’s size, shape, and star formation activity. As galaxies traverse through these filamentary structures, they may also acquire new material from their surroundings, further enriching their stellar populations and chemical compositions.
Challenges in Studying Galaxy Alignment Filaments
Despite significant advancements in observational techniques and theoretical modeling, studying galaxy alignment filaments presents several challenges. One major hurdle is the difficulty in accurately mapping dark matter distributions due to its non-luminous nature. While gravitational lensing provides some insights into dark matter halos, it remains challenging to obtain a comprehensive picture of how these halos influence galaxy alignments.
Additionally, distinguishing between genuine filamentary structures and random alignments can be complex. Researchers must employ sophisticated statistical methods to analyze large datasets while accounting for potential biases introduced by observational limitations. The sheer scale of the universe also poses challenges; capturing filamentary structures requires extensive surveys that span vast distances and encompass numerous galaxies.
Current Research and Discoveries in Galaxy Alignment Filaments
Current research on galaxy alignment filaments is vibrant and multifaceted, with scientists employing various methodologies to deepen their understanding. Recent studies have utilized machine learning algorithms to analyze large datasets from astronomical surveys, enabling researchers to identify filamentary structures more efficiently. These innovative approaches have led to new discoveries regarding the properties and dynamics of galaxy alignments.
Moreover, collaborations between observational astronomers and theoretical physicists have yielded valuable insights into how galaxy alignment filaments evolve over time. By combining observational data with simulations, researchers can test hypotheses about filament formation mechanisms and their impact on galaxy evolution. This interdisciplinary approach has opened new avenues for exploration, allowing scientists to refine existing models and propose new theories regarding cosmic structure.
Future Prospects for Studying Galaxy Alignment Filaments
The future prospects for studying galaxy alignment filaments are promising, driven by advancements in technology and observational capabilities. Upcoming telescopes such as the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) are expected to provide unprecedented views of distant galaxies and their environments, allowing researchers to probe filamentary structures with greater detail than ever before. These observations will likely enhance our understanding of how galaxies interact within filaments across different epochs in cosmic history.
Additionally, ongoing developments in computational astrophysics will enable more sophisticated simulations that incorporate complex physical processes governing galaxy formation and evolution. As researchers continue to refine their models and integrate new observational data, they will be better equipped to unravel the mysteries surrounding galaxy alignment filaments and their role in shaping the universe.
Implications of Galaxy Alignment Filaments for Cosmology and Astrophysics
The study of galaxy alignment filaments carries significant implications for cosmology and astrophysics as a whole. Understanding these structures provides insights into fundamental questions about dark matter’s nature, galaxy formation processes, and the overall dynamics of cosmic evolution.
Furthermore, insights gained from studying galaxy alignment filaments can inform our understanding of cosmic expansion and large-scale structure formation. By examining how galaxies align along these filaments over time, scientists can glean information about the underlying physics driving cosmic evolution, ultimately contributing to a more comprehensive picture of our universe’s history.
Conclusion and Summary of Key Findings about Galaxy Alignment Filaments
In conclusion, galaxy alignment filaments represent a crucial aspect of cosmic structure that offers valuable insights into the formation and evolution of galaxies within the universe. Through a combination of theoretical frameworks and observational evidence, researchers have established that these elongated structures are shaped by gravitational interactions involving dark matter. The impact of galaxy alignment filaments extends beyond mere organization; they play a significant role in influencing star formation rates, morphological characteristics, and interactions among galaxies.
As challenges persist in studying these complex structures, ongoing research continues to yield new discoveries that deepen our understanding of cosmic evolution. With advancements in technology and interdisciplinary collaboration paving the way for future exploration, scientists are poised to uncover even more about the intricate web that connects galaxies across vast distances. Ultimately, the implications of studying galaxy alignment filaments extend far beyond individual galaxies; they contribute to our broader understanding of cosmology and astrophysics as we seek to unravel the mysteries of our universe.
Recent studies on galaxy alignment and filament torques have shed light on the intricate dynamics of cosmic structures. For a deeper understanding of these phenomena, you can explore the article on cosmic ventures that discusses the implications of filamentary structures in the universe. Check it out here: Galaxy Alignment and Filament Torques.
WATCH THIS! 🧠 The Universe Is A Brain. And It’s Having A Stroke.
FAQs
What is galaxy alignment?
Galaxy alignment refers to the observed phenomenon where the orientations or spins of galaxies are correlated with each other or with the large-scale structures of the universe, such as cosmic filaments and sheets.
What are cosmic filaments?
Cosmic filaments are massive, thread-like structures composed of dark matter, gas, and galaxies that form part of the cosmic web, connecting clusters and superclusters of galaxies across the universe.
How do filaments influence galaxy alignment?
Filaments exert gravitational torques on galaxies forming within or near them, which can influence the spin direction and orientation of galaxies, leading to alignment patterns along the filament’s axis.
What role do torques play in galaxy alignment?
Torques are twisting forces caused by gravitational interactions that can alter the angular momentum of galaxies. In the context of filaments, these torques can align galaxy spins with the filament’s structure.
Why is studying galaxy alignment important?
Understanding galaxy alignment helps astronomers learn about the formation and evolution of galaxies, the influence of large-scale structures, and provides insights into the distribution of dark matter in the universe.
How is galaxy alignment observed?
Galaxy alignment is studied through astronomical surveys that measure the shapes, orientations, and spins of galaxies, often using optical and radio telescopes, combined with simulations of cosmic structure formation.
Does galaxy alignment affect cosmological measurements?
Yes, intrinsic alignments of galaxies can contaminate weak gravitational lensing signals, which are used to study dark energy and dark matter, so understanding and modeling alignment is crucial for accurate cosmological analyses.
Are all galaxies aligned with filaments?
Not all galaxies show alignment; the degree of alignment depends on factors such as galaxy type, mass, environment, and the scale of the filamentary structure.
What theories explain galaxy alignment in filaments?
The tidal torque theory is a leading explanation, suggesting that gravitational tidal forces from surrounding matter during galaxy formation impart angular momentum, aligning galaxies with filaments.
Can simulations reproduce galaxy alignment?
Yes, cosmological simulations that include dark matter, gas dynamics, and galaxy formation processes can reproduce observed galaxy alignment patterns, helping to test and refine theoretical models.
